Lesson Six: Parking (4.6)
Maneuvering your vehicle in confined spaces can be intimidating. Using reference points, inching speed, and the correct procedures allows you to be successful in any parking situation. The following parking maneuvers have several elements in common such as reference points, side and forward positions, and slow speed. SIM still applies.
Pulling into a space on the left or right can be angled or straight lines.
Forward Angle Parking – 45 degrees
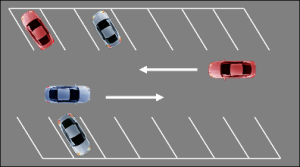
Park
- Check front & rear.
- Signal right.
- Align side position 6 from the parking space.
- When you can see the center of the parking space without your vision cutting across the line, target center of the space and slowly enter the space.
- Straighten car and tires and stop at forward position.
- When parked to the right as illustrated, the curb will appear forward of the left corner post. When parked to the left, the curb will appear forward of the right corner post.
- Secure the vehicle.
Exit
- Shift to reverse
- Search the rear (360°).
- Back slowly
- Check all corners and begin to turn the wheel when the rear pivot point aligns with the bumper of the vehicle on the right and the side mirror aligns with the bumper of the vehicle on the left.
- Continue backing until you are clear of the surrounding vehicles and stop.
- Straighten the tires.
- Shift to drive.
Forward Perpendicular Parking – 90 degrees
Park
- Check front & rear.
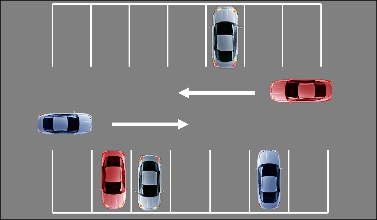
- Signal right.
- Align side position 6 (6-8 feet) from the parking space.
- When you can see the center of the parking space without your vision cutting across the line, slowly enter the space.
- Target the center of the space.
- Straighten car and tires and stop at forward position.
- Secure the vehicle.
Exit
- Shift to reverse
- Search the rear (360°).
- Back slowly
- Check all corners and begin to turn the wheel when the side mirror aligns with the bumper of the vehicle on the left.
- Continue backing until you are clear of the surrounding vehicles and stop.
- Straighten the tires.
- Shift to drive.
 Parking Angle and Perpendicular
Parking Angle and Perpendicular
Back-In Parking
Backing into a space can be angled or straight lines.
What are the advantages of back-in parking?

Back-In Angle Parking – 45 degrees
Park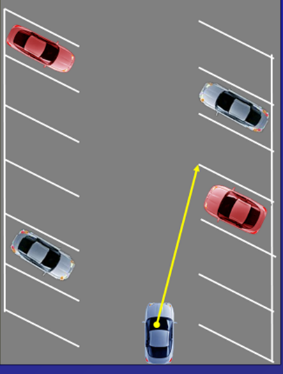
- Check front & rear.
- Signal right.
- Align side position 3 (3 feet) from the parking space.
- Pull past the space and stop.
- Shift to reverse and search in all directions (360°).
- Target and back slowly.
- Turn the wheel when the pivot point aligns with space.
- Straighten the wheels, back slowly, and stop when you reach the rear position and secure the vehicle.
Exit
- Shift to drive.
- Check traffic.
- Signal.
- Pull out when clear.
Back-In Perpendicular Parking – 90 degrees
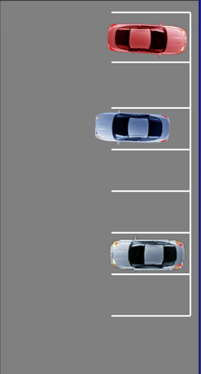
Park
- Check front & rear.
- Signal right.
- Align side position 3 (3 feet) from the parking space.
- Pull forward until your body is aligned in the center of the space.
- Select 45° Target – over outside edge of the driver’s side mirror.
- Check traffic, turn wheel fully left and creep forward until on target.
- Turn the wheel fully to the right, search in all directions (360°), shift to reverse and back slowly until vehicle is perpendicular with the space.
- Stop at the rear position and secure the vehicle.
Exit
- Shift to drive.
- Check traffic.
- Signal.
- Pull out when clear.
 Back-in Angle and Perpendicular Parking
Back-in Angle and Perpendicular Parking
Back-In Parallel Parking
Parallel parking is backing into a space parallel to the curb, usually between two vehicles.
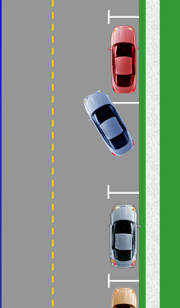
Park
- Check front & rear.
- Signal right.
- Align side position 3 (3 feet) from the parking space.
- Identify 1½ car lengths of available space.
- Stop when your rear bumper is even with the front vehicles rear bumper.
- Turn wheel fully to the right, shift to reverse, search 360°.
- Back slowly until you see the inside corner (curbside) of the car in back in your left rearview mirror and stop.
- Straighten your wheels and continue to inch back until your right front tire is at the corner of the car in front of the space.
- Stop and turn the wheels all the way to the left.
- Back until the car is parallel to the curb, stop, straighten wheels and pull up until centered.
- Stop and secure the vehicle.
Exit
- Search 360⁰ and back up if you need space to the front.
- MSMOG procedure
- Turn wheel fully left and enter your lane
- Check rear and cancel signal.
 Parallel Parking
Parallel Parking
Essential Questions
-
What is the correct side position for forward/angle/perpendicular parking?
-
What is the correct side position for back in perpendicular and parallel parking?
-
Where is the rear position when backing into a space?
A point on the vehicle, viewed from the driver’s seat that relates to some part of the roadway.
An acronym used for searching and space management principles. It stands for Search, Identify, and Manage.