Advertising as Persuasion

“What you call love was invented by guys like me to sell nylons.” — Don Draper, fictional advertising executive from the AMC series Mad Men
Advertising is a relatively straightforward process, right? Companies develop brands and specific products they want to sell. They need to make consumers aware of their brands, products and those products’ features, so they develop creative campaigns to promote them and often pay ad agencies to do the creative work and place the ads in front of mass audiences. The basic definition of advertising is a message or group of messages designed with three intentions: to raise awareness in the population about brands, products and services; to encourage consumers to make purchases; and, ultimately, to inspire people to advocate for their favorite brands. A brand advocate is someone who is so supportive of a product or service that they publicly encourage others to buy it. There are paid brand advocates, of course, but in a networked communication environment, even unpaid individuals with modest followings can become influencers — people who promote products on their social media streams. Consumers who have been so successfully persuaded to purchase and enjoy a product that they try to persuade others to buy it too extend the reach of advertising potentially exponentially.
A company is a business entity that produces several types of product, whereas a brand is a term used to label a specific product or a limited family of products. It is important to differentiate between the two. For example, PepsiCo owns the Pepsi brand but also Frito Lay, Gatorade and Quaker, among others. Under the Pepsi brand, there are several products such as Diet Pepsi, Pepsi Wild Cherry and many other variations around the world. Advertising most often focuses on brands and products rather than the companies and large corporations that own them.
Advertising Defined
On one level, advertising is a simple concept. Mass media professionals craft messages to help sell products by raising awareness and pushing people to make actual purchase decisions, but in the network society and the age of targeted marketing, the ability to reach individual consumers who fit precise sets of characteristics is incredible. More is expected of advertisers than to put interesting messages in front of the “right people” based on general demographics. Brands may advertise during certain TV shows or publications to reach a particular type of media consumer. This more traditional form of mass media advertising is still a multibillion-dollar industry, but with data-driven targeting capabilities, brands can reach people based not only on general demographic characteristics but on specific behaviors as well. The combination of detailed demographic information, search and digital media usage behaviors and physical world behaviors (such as whether someone has entered a Walmart or Macy’s in the past week) makes advertising in the information age more powerful, sometimes more meaningful and often more ethically questionable than in the past. The level of targeting that is possible is incredible and would have been unimaginable 20 years ago. Advertising has always been about tapping into consumers’ existing needs or about creating a need and inserting a product to fill it. Now, there is a greater ability than ever to identify and create a need not only for interested members of a mass audience but also for specific individuals in real time based on their online and physical world behavior.
The History of Advertising
Before delving into a discussion about the future of advertising, it might help to survey the history of the field. Advertising in the modern sense emerged between the mid-19th and early-20th centuries. At the same time that the concept of brands was developing, mass-media platforms such as daily newspapers and radio broadcasts grew their audiences and spread their influence geographically. Corporations, conveniently, grew large enough to have massive budgets to spend on advertising. The promotion of products dates back thousands of years, but the modern advertising explosion tracks explosive growth in industrial manufacturing from roughly the mid-1800s through the entire 20th century.

HubSpot has a deck of 472 slides that presents a narrative about the history of advertising. Some highlights are referenced here. One key point made in this visual history is that non-branded newspaper ads would often outnumber branded ads in the early days of the newspaper industry. As uniformity in mass-produced goods became the norm and brand differentiation became possible, so did the need to communicate it.
Ayer & Son is credited with being the first ad agency to work on commission. In other words, it is known as the first modern ad agency. It was founded in Philadephia in 1869. Today there are about 500,000 ad agencies in the world of all shapes and sizes. They employ ever-evolving techniques to try to stay ahead of information weary consumers.
Categorizing Advertising Methods
From the mid-20th century on, advertisers conceptualized their work by breaking it down into one of two strategic categories: “above-the-line” and “below-the-line” methods. Put simply, “above the line” (ATL) refers to methods of advertising that target mass audiences on mass media platforms with messages usually designed from a one-to-many point of view. Often, “above the line” implies that the ad or ad campaign — a series of related ads meant to work in tandem — appears on legacy media platforms. “Legacy media” refers to platforms in existence before the transition to digital. ATL campaigns most often include television, radio and print ads as well as sponsorships. A sponsorship is when a company pays to support an event or a mass media production in exchange for having its brand promoted alongside the activity or content. The organizing concept for ATL advertising, as the term is used today, is that the ads target a mass audience primarily on “legacy” media platforms.

“Below the line” (BTL) advertising refers to more one-on-one marketing approaches which can include targeted social media campaigns, direct mail marketing, point-of-sale ads, coupons and deals, and email and telemarketing appeals. This is not an exhaustive list of ATL or BTL methods, but these examples demonstrate that ATL has more in common with the concept of mass communication introduced in earlier chapters, and BTL has more in common with interpersonal communication, also as previously discussed. This is not to say that BTL messages are crafted one at a time for individual consumers. Rather, the tone, style and method of dissemination of BTL advertising are more personal.
In the 20th century, the term ATL advertising was associated with ad agency work (mostly mass media campaign ads), whereas BTL advertising referred to pamphlets, point-of-sale marketing and other relatively “small” tasks that ad agencies typically did not handle. Now, there are ad agencies of all sizes, and even very large agencies might do BTL marketing. Online advertising and social media marketing have made it possible to target people with personal messages but still purchase the ads on a massive scale. Thus, advertising can be massively individuated — that is, produced for mass audiences but having the appearance of personalized messages — much like social media content. The profit in BTL marketing comes from reaching large audiences with tailored messages at specific times in relation to their previous purchasing and shopping behaviors. So much data exists on individual users and on the behavior of similar people who have made similar purchases that advertisers can try to target people at precisely the right moment to influence their purchase decisions.
ATL and BTL advertising can work hand in hand. Think of a summer soft drink promotion advertised on television and on the radio (ATL) that is also backed up with neighborhood-specific billboards and hyper-targeted Twitter messages with surprise prizes given out (BTL). BTL messages still reach large numbers of people, but they are by definition more tailored than ATL ads. An individual ad in a BTL context may not cost as much as a massive ad buy facilitated by an agency that primarily does ATL advertising; however, BTL advertising can still be costly for advertisers and profitable for ad agencies in the aggregate. For example, an ad agency that does not typically manage multimillion-dollar television ad buys might still put together hundreds of thousands of dollars in targeted social media ads. Rather than displaying one commercial for several months, the BTL social media campaign might be made up of dozens of targeted videos, tweets, influencer posts and online ads. Often software algorithms are used to decide who sees which targeted ad and when.
The Advertising Funnel and Other Key Concepts
At its heart, advertising is a matter of raising awareness, creating a deeper interest in a product, and encouraging consumers to desire to make a purchase and ultimately to take action. Professional communicators tailor messages in relation to the advertising funnel or purchase funnel, as shown in the image on the left. Brands, either on their own or with the help of advertising agencies, target audiences in different ways at specific points along the funnel to reach their strategic goals. For example, if an unknown brand launches a new product, people need to be made aware of both the brand and product. The brand may need to establish itself with an awareness campaign. If Nike introduces a new Air Jordan, the branding is easily handled. The top of the funnel areas of awareness and interest will not need as much focus as the decision and action areas, the “down funnel” aspects of a campaign for a well-known and well-loved brand.
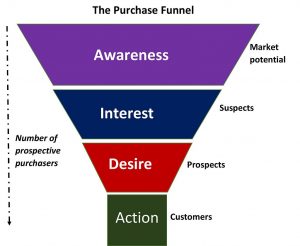
Another way to think of this is as a pathway a potential customer makes, also known as the consumer journey. First, the consumer needs to be made aware of the brand and its products. Then, they might take an interest in a particular product as they learn more about its features. They need to move from being interested to desiring a product if they are going to make the purchase. Ultimately, from the advertiser’s point of view, the goal is not only to move the consumer to purchase the product but also to inspire them to advocate for the brand. This is not conceptually complicated. The idea is to move people in straightforward steps toward desired behaviors; however, there are complex processes of cognition and persuasion that underlie consumer decisions.
Consumer behavior is about as unpredictable as other forms of human behavior. There are also ethical concerns. If a product or service proves to be harmful, advertisers and public relations professionals have to decide if and when they will stop marketing the brand. Advertising is challenging enough when products do not raise ethical dilemmas. Promoting harmful products can be damaging socially, professionally and personally. Thus, the world of consumer advertising in the mass media is more complex than the funnel makes it seem, although it is an essential strategic model in the industry.
Content Marketing
Content marketing refers to a common practice where brands produce their own content, or hire someone else to produce it, and then market that information as an alternative to advertising. It still moves people along the purchase funnel, but there is usually added value in this type of content. If an advertisement for a mattress describes its features and price, a blog funded by the mattress brand might compare the pros and cons of many different mattresses, perhaps with a bias for the brand. It isn’t always pretty. Content produced for a brand should ethically be labeled as sponsored, but it is not always done. In cases when consumers have discovered that trusted sources were content marketers rather than independent reviewers, the revelations have created public relations problems for the brands. Content marketing done ethically offers financial transparency while providing valuable information and an emotional connection to the product for consumers. It can take the form of blog posts or entire blogs. Such marketing is usually optimized for search engines, which is to say the posts are written to attract search engine attention as well as outside links, which also alerts search engines that this content is valuable. Done well, branded content can be seen as more authentic than advertising content, and it can be cheaper to produce and disseminate. It is difficult to do well, of course.
The most common types of content created in this context besides blog content are social media profiles and posts, sponsored content in social media spaces and even viral video and meme chasing. Brands might have their own social media profiles, or they might support social media influencers to promote their products in a sponsored way. Brands might also use their influencer teams or their own internal marketing teams to follow viral social media trends and to create memes. In a sense, content marketing allows a brand to create a more human profile in digital spaces. In this manner, brands can engage with potential and repeat customers. Brands can foster relationships and encourage brand advocacy among people not being paid to promote their products. Many brands use this form of marketing to engage consumers on a deep level and to offer information and emotion that might not be present in other forms of advertising.
